Is there proof that your hand sanitizer is effective?
Home » Is there proof that your hand sanitizer is effective?
Hand sanitizer gels contain multiple ingredients with ethanol or isopropanol as the primary active ingredient for antiseptic purposes. Hand sanitizer gels that are alcohol based have a recommended alcohol concentration of 60-95% to be considered effective.1 Currently, shortages on hand sanitizer products have pushed companies who normally do not manufacture hand sanitizer products to start production. In order to ensure hand sanitizer products are being produced properly, the proper analytical tools for product investigation are necessary.
Eurofins EAG Materials Science is equipped with the necessary tools and techniques to examine hand sanitizer gel products for their primary ingredients by Gas Chromatography with Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR). This note demonstrates the abilities that Eurofins EAG has to quickly and accurately screen hand sanitizer products to ensure these types of products meet the requirements for effectiveness.
DISCUSSION
In this study, the objective was to screen five commercial hand sanitizer gels for their main ingredients by GC/MS and FT-IR. A list of the ingredients commonly found in hand sanitizers is shown in the Table 1A.
Each common inactive ingredient in hand sanitizer gels serves a specific purpose. Water acts as a solvent and is necessary to allow the active ingredient alcohol to penetrate bacterial cells in order to kill them. Glycerin and propylene glycol are humectants to help prevent the loss of moisture in the skin. Isopropyl myristate is an emollient. Along with Vitamin E acetate, isopropyl myristate helps smooth skin. Carbomer is a thickening agent that causes the gel-like texture in hand sanitizers, and triethanolamine functions as a pH adjuster as well as promoting emulsification.
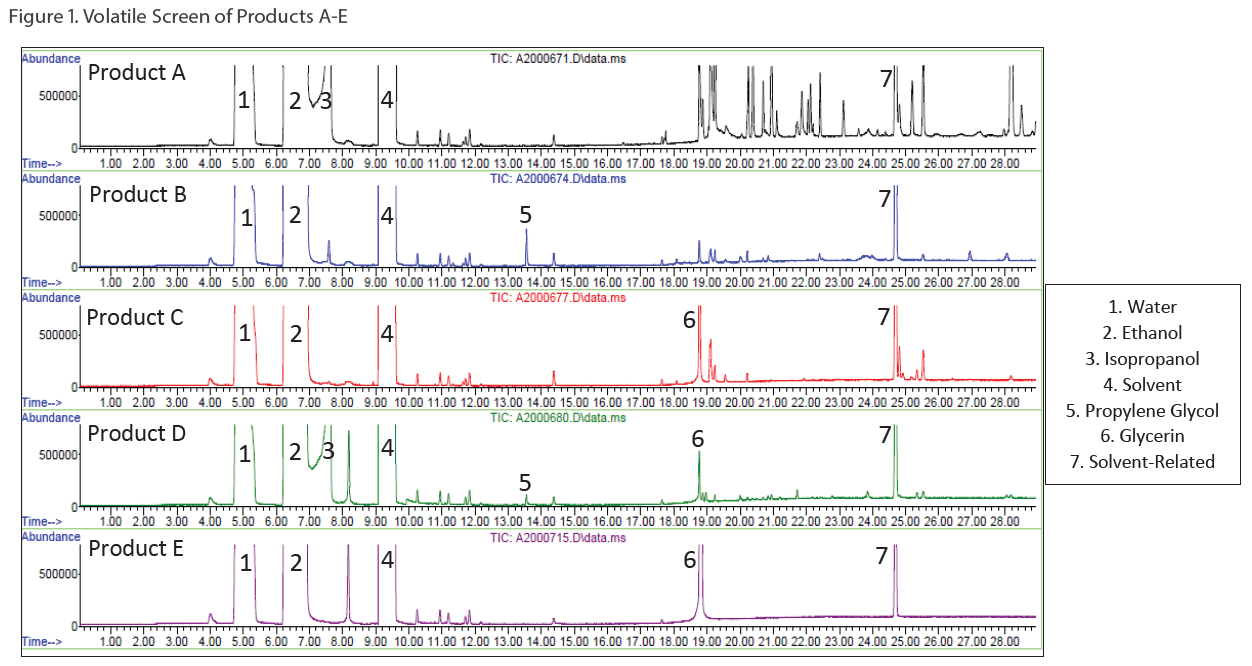
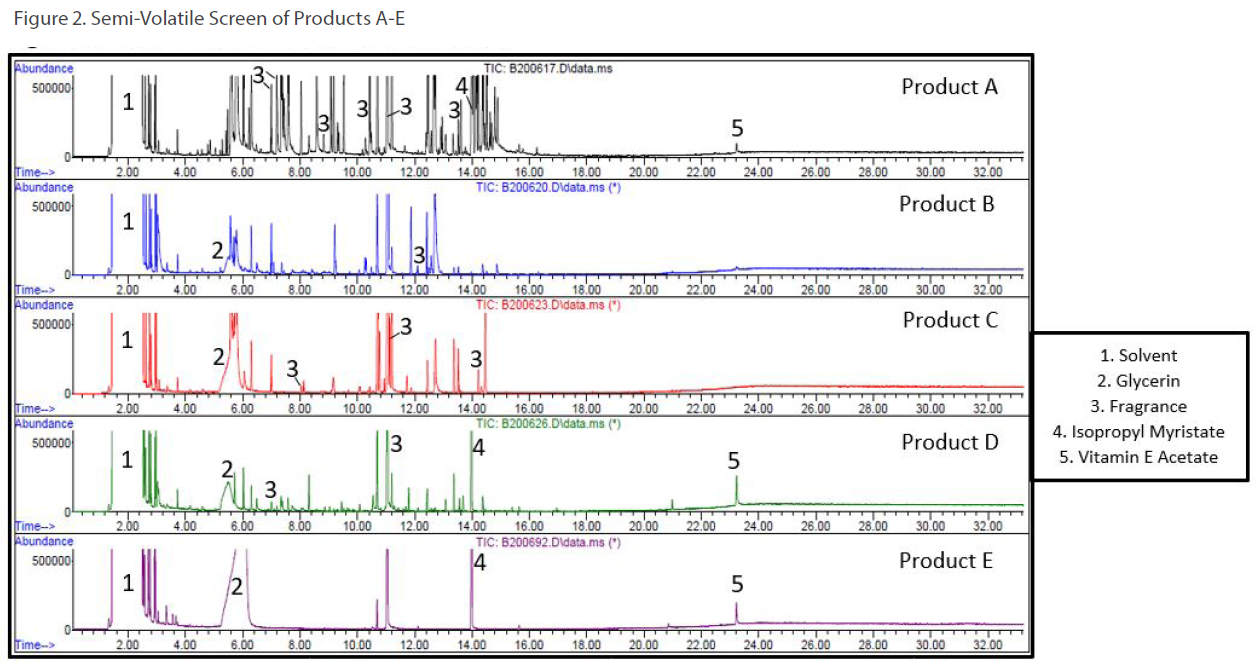
Two types of screening methods by GC/MS were utilized: 1) a volatile screening method for ingredients like ethanol, isopropanol and propylene glycol (see Figure 1) and 2) a semi-volatile screening method for ingredients like glycerin, Vitamin E acetate, and isopropyl myristate (see Figure 2).
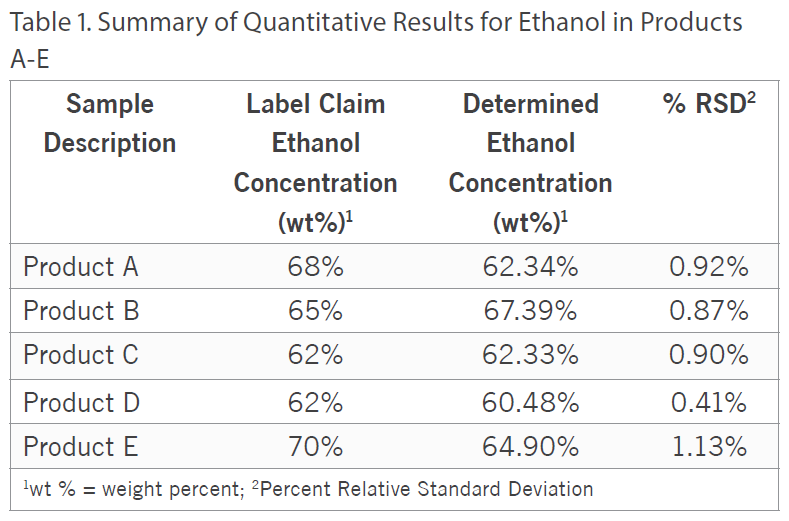
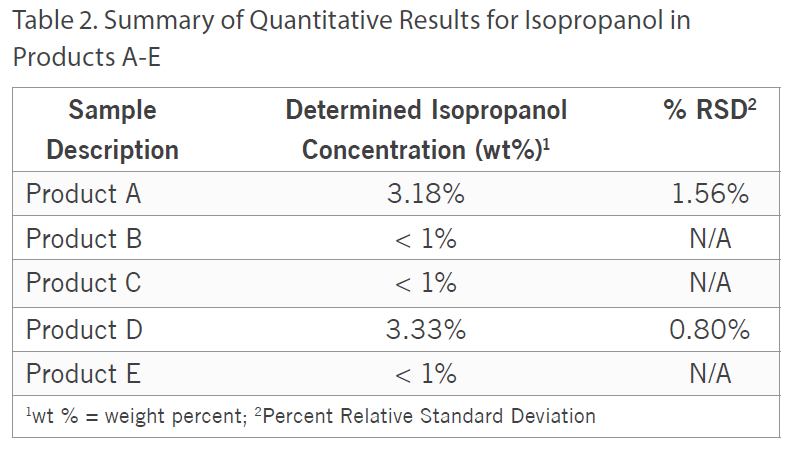
Additionally, besides qualitatively screening the samples, the ethanol and isopropanol content was quantified in all five of the samples by Gas Chromatography with Flame Ionization Detection (GC/FID) using analytical reference standards for calibration. For the ethanol quantitation, Product D was fortified with a known amount of ethanol to assess accuracy and the spike recovery was observed to be 101%.
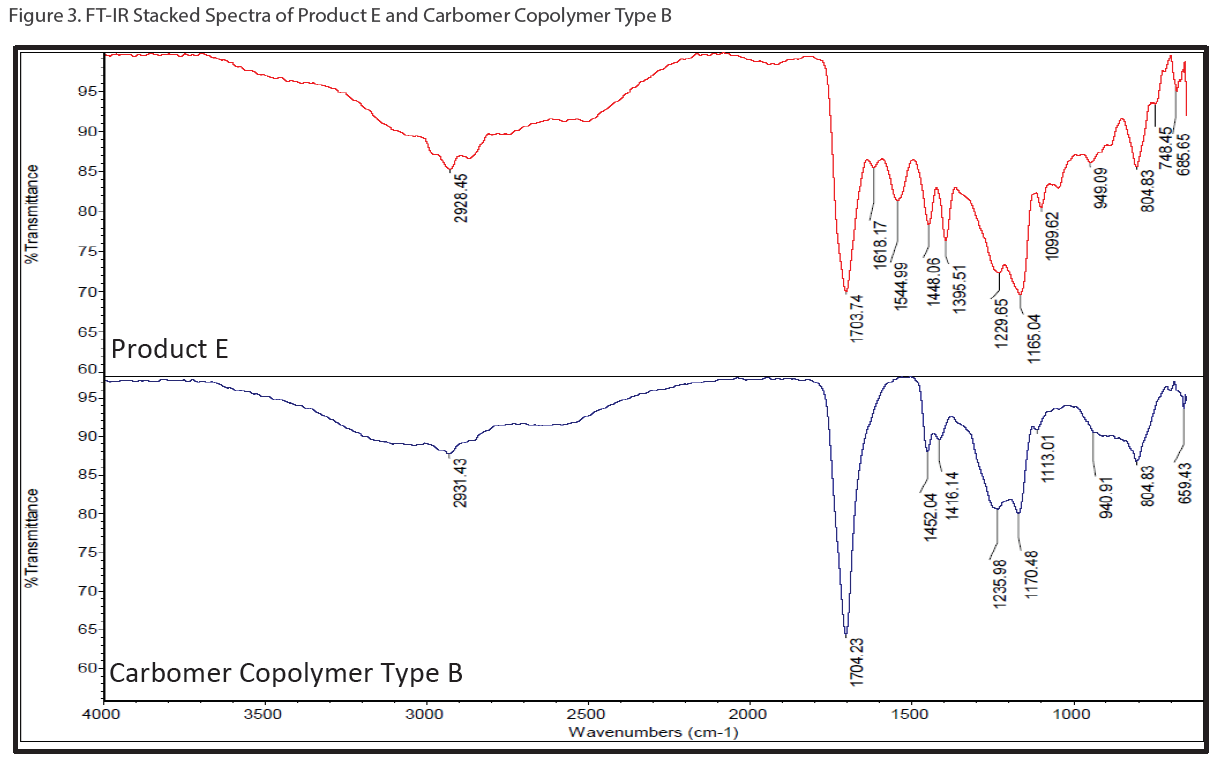
Not every ingredient in hand sanitizer gels can be analyzed by GC/MS. To elucidate the polymeric portion of hand sanitizer gels (i.e. carbomer or polyacrylic acid), a customized series of solvent extractions was performed to isolate the carbomer followed by FT-IR to confirm its presence. Figure 3 shows stacked FT-IR spectrum of Product E (red trace) and a carbomer standard (purple trace).
Additionally, besides an FT-IR screen of Product E for carbomer, the carbomer content in this product was gravimetrically determined. Table 4 below summarizes these results.
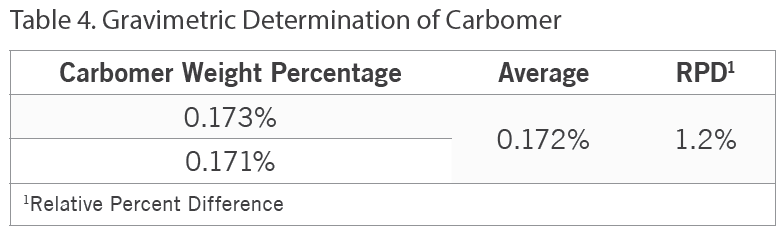
Would you like to learn more about hand sanitizer analysis?
Contact us today for your hand sanitizer analysis needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.
