NanoIR
Home » Our Techniques » Spectroscopy » NanoIR
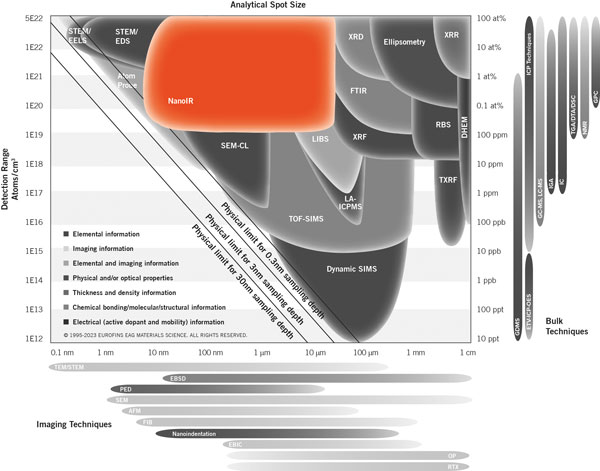
Atomic force microscope based infrared spectroscopy (AFM-IR, nanoIR) is an effective analytical technique for identifying the “chemical family” of a substance with high spatial resolution. Typically, organic and polymeric compounds (and, to a lesser degree, inorganic compounds) produce a unique “fingerprint” IR spectrum that is reflective of the chemical structure of the compound.
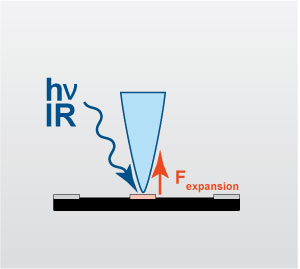
Similar to Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), nanoIR measures the absorbance of infrared light by a sample and generates a spectrum based on the functional groups in the material. However, FTIR is typically limited to a spatial resolution on the order of tens of microns, and samples that are too thick cannot always be directly analyzed without additional preparation. These limitations are bypassed in nanoIR by utilizing the AFM cantilever as a near-field detector for infrared absorption in the sample. The detection of IR absorbance is localized to the cantilever tip (~30 nm radius), subsequently resulting in spatial resolutions down to tens of nanometers. Briefly, if a material absorbs infrared light at a particular frequency, there is a subsequent thermal excitation and expansion of the sample, which is detected by the AFM cantilever. Measuring the cantilever response as a function of laser frequency generates a spectrum that is proportional to the infrared absorption of the material. The resulting spectra are often highly similar to those obtained via FTIR, enabling compound/family identification via comparisons to EAG’s extensive reference databases.
Ideal Uses of NanoIR
- Identification of organic contaminants (e.g. particles, residues) on the micro and nanoscales
- Characterization of organic layers in thin cross sections
- Mapping distribution of different chemical components
- Correlation of composition to topographical, mechanical, or electrical properties (AFM, NI)
- Characterization and identification of complex mixtures of materials
Strengths
-
High lateral spatial resolution: <20-50 nm
- Higher surface sensitivity relative to FTIR
- Capable of identifying organic functional groups and often specific organic compounds
- Extensive spectral libraries for compound and mixture identifications
- Ambient conditions (vacuum is not necessary; applicable for semi-volatile compounds) but typically purged with dry air (~5% relative humidity)
- Complementary to compositional techniques such as Raman spectroscopy and FTIR
Limitations
- Only specific inorganic species exhibit an IR spectrum (for example: yes: silicates, carbonates, nitrates and sulfates; no: titania, oxides, simple cations and anions, e.g., Na+ and Cl–)
- Smaller spectral range than FTIR
- Typically not a quantitative technique without extensive standards
- Thin samples on highly absorbing substrates or contamination from handling/storage may show absorbances that can potentially overwhelm the signal from the actual sample
- Samples coated in highly reflective metals (Au, Pt, Ir) cannot be analyzed
Potential problems with extremely rough or oddly shaped samples, solutions, or low viscosity liquids
NanoIR Technical Specifications
- Signal Detected: Topography and infrared absorption
- Information provided: Molecular functional groups (NOT elements)
- Detection Limits: 1-10 wt% (quantification of known components);
5-20 % (identification of unknown components) - Depth Resolution: ~30-200 nm
- Imaging: Single wavenumber chemical maps + standard AFM imaging modes (height, phase)
- Lateral Resolution/Probe Size: 10-50 nm
- Maximum analysis region: 80 × 80 µm2
- Spectral range: 1860-760 cm-1 (1 cm-1 resolution),
2680-4020 cm-1 (5 cm-1 resolution)
In conclusion, EAG offers NanoIR services combining the nanometer scale spatial resolving capabilities of AFM with the chemical characterizing capabilities of infrared spectroscopy. Moreover, you can count on fast turnaround times, accurate data and person-to-person service, ensuring you understand the information that you receive.
Would you like to learn more about NanoIR?
Contact us today for your NanoIR needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.