Laser Diffractometry
Home » Our Techniques » Laser Diffractometry
Particle Size Distribution Analysis Using Laser Diffractometry
EAG Laboratories offers a full portfolio of particle size measurement techniques, covering a range of more than six orders of magnitude. Laser diffractometry is an analytical technique to determine the particle size distribution of powders and suspensions in the 0.02 µm – 2000 µm range. Typical applications include: raw materials for glass production, materials for 3D-printing, phosphors and inks.
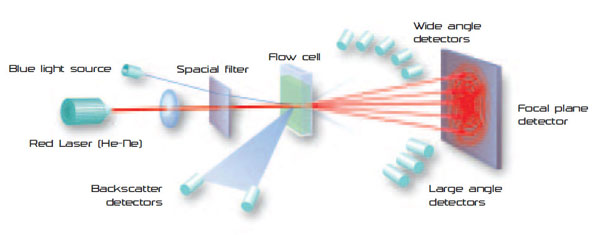
A suspension is pumped through a measuring cell and is subsequently illuminated by a laser beam. When particles of different sizes pass a laser beam, they cause the laser light to be scattered at angles that are inversely proportional to the particle size. The angular scattering intensity data is analyzed to calculate the size of the particles, using the Mie scattering or Fraunhofer diffraction theory.
Laser Diffractometry measuring principle is pictured below.
Ideal Uses of Laser Diffractometry
- Particle size distribution analysis of suspensions and powders
Strengths
- Wide dynamic range (0.02 µm – 2000 μm)
- Applicable to powders and suspensions
Limitations
- Refractive index and absorption of the material must be known for samples with particles smaller than 50 µm
- Sample preparation is very important. If the sample is poorly prepared (unrepresentative or badly dispersed) then the data will be incorrect
Laser Diffractometry Technical Specifications
- Particle size range: 0.02 μm – 2000 µm
- Sample amount: dependent on the particle size
- Measurement principle: Mie scattering and Fraunhofer diffraction
Would you like to learn more about using Laser Diffractometry?
Contact us today for your Laser Diffractometry needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.