Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Home » Our Techniques » Spectroscopy » FTIR
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is an effective analytical technique for quickly identifying the “chemical family” of a substance. Typically, organic and polymeric compounds (and, to a lesser degree, inorganic compounds) produce a “fingerprint” IR spectrum, which can be compared to EAG’s extensive reference database, and the unknown component’s chemical family or actual identity may be determined.
FTIR measures the absorbance of infrared light by a sample and generates a spectrum based on the functional groups in the material. In addition to typical sample preparation methods (such as micro-extraction, dilution, KBr pellet and mulling techniques), EAG also utilizes various Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) accessories, which allows insoluble or multi-layer samples to be examined directly.
Ideal Uses of FTIR
- Characterization and identification of complex mixtures of materials, including gases, liquids and solids
- Identification of organic contaminants (e.g. particles, residues) on the macro and micro scales
- Quantification of Oi in Si wafers and H in SiN, SiON and a-Si thin films (Si-H vs. N-H)
- Medical device chemical characterization via ISO 10993:18
Strengths
- Capable of identifying organic functional groups and often specific organic compounds
- Extensive spectral libraries for compound and mixture identifications
- Ambient conditions (vacuum is not necessary; applicable for semi-volatile compounds)
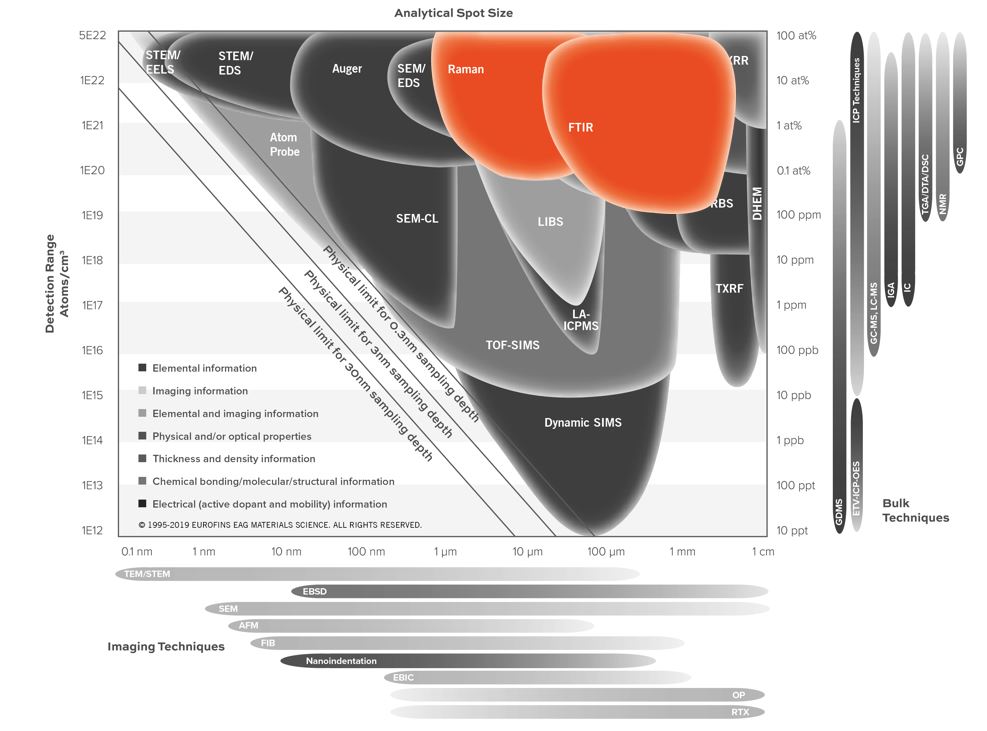
- Minimum (limit of detection) analysis area: ~15-50 µm. Rule-of-thumb: if you can see the sample by eye, it most likely can be analyzed.
- Can be quantitative with appropriate standards and uniform sample thicknesses
- Complementary to Raman spectroscopy
Limitations
- Firstly, limited surface sensitivity (typical limit of detection is a film thickness of 100 nm)
- Only specific inorganic species exhibit an FTIR spectrum (for example: yes: silicates, carbonates, nitrates and sulfates; no: titinia, oxides, etc.)
- Sample quantitation requires the use of standards
- Glass absorbs infrared light and is not an appropriate substrate for FTIR analysis
- Water also strongly absorbs infrared light and may interfere with the analysis of dissolved, suspended or wet samples
- Simple cations and anions, e.g., Na+ and Cl–, do not absorb FTIR light and hence cannot be detected by FTIR. Identification of mixtures/multiple sample components may require additional laboratory preparations and analyses.
- Lastly, FTIR cannot analyze metals that reflect light
FTIR Technical Specifications
- Signal Detected: Infrared absorption
- Elements Detected: Molecular functional groups (NOT elements)
- Detection Limits: 1-10 wt% (quantification of known components); 5-20 % (identification of unknown components)
- ATR Depth Resolution: ~0.1-1 micron
- Transmission FTIR: Infrared light passes through the entire sample
- Imaging: No mapping for FTIR
- Lateral Resolution/Probe Size: > 15-50 µm
In conclusion, EAG offers our customers FTIR services to analyze many materials. Moreover, you can count on fast turnaround times, accurate data and person-to-person service, ensuring you understand the information that you receive.
Would you like to learn more about using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy?
Contact us today for your Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.