
When Metal Fails: How Metallurgy Helps Us Understand Bridge Collapses
Learn about how metallurgy plays a critical role in infrastructure safety, revealing how corrosion, fatigue, and poor material choices can lead to catastrophic collapses.
Home » Frequently Asked Questions About In Vitro Irritation and Cytotoxicity Testing
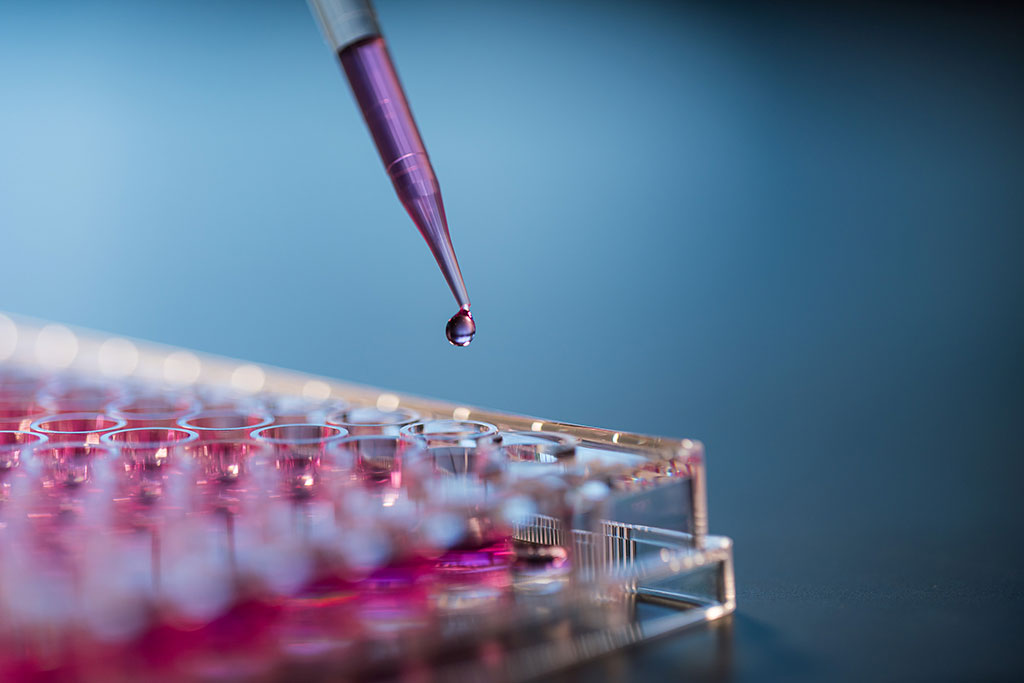
Biocompatibility assessments are a battery of tests performed to evaluate a product, medical device, or other material for the risk of biological hazards. The first test performed is typically a cytotoxicity evaluation. This is done by preparing an extract of the sample to treat a monolayer of healthy mammalian cells in vitro. Results of this assay can indicate the potential toxicity risk a product carries without testing on animals.
Irritation is a localized non-specific inflammatory response to a single, repeated, or continuous application of a substance or material. The in vitro irritation test involves an extraction in physiologically relevant solvents. These extracts are applied to a reconstructed human epidermis model which contains the major layers of cells that are found in a true human epidermis. Death of the cells in this model after exposure to the extracts collected from a product indicate that an irritating substance was leached off the material and poses a risk of adverse reactions in the end user.

Learn about how metallurgy plays a critical role in infrastructure safety, revealing how corrosion, fatigue, and poor material choices can lead to catastrophic collapses.

TEM, STEM and AC-STEM techniques deliver high resolution images providing a detailed view of a material or product.

Wednesday, October 15, 2025
Presenters from EAG and MCRA will cover the many ways to approach study design from chemistry, toxicology, and regulatory perspectives.
Besides images provided by SEM and TEM, different attachments can be added to reveal crystalline information, including (SEM-EBSD) and TEM (TEM-PED).
To enable certain features and improve your experience with us, this site stores cookies on your computer. Please click Continue to provide your authorization and permanently remove this message.
To find out more, please see our privacy policy.