Using STEM EELS to Probe Local Bonding Environment in VCSEL Oxide Apertures
Home » Using STEM EELS to Probe Local Bonding Environment in VCSEL Oxide Apertures
STEM EELS provides a method to locate secondary phases that could possibly
correlate to degraded performance.
Vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSELs) have become an integral technology in optoelectronics ranging from consumer electronics to medical applications. Achieving high reliability and performance requires fine control over growth and device fabrication. One important aspect is precise oxidation of the aperture layer, responsible for current confinement. Improper aperture oxidation can lead to high stress or introduce unintended defects ultimately resulting in failure. Here, we present a study using STEM EELS to provide a method for measuring differences in oxygen bonding.
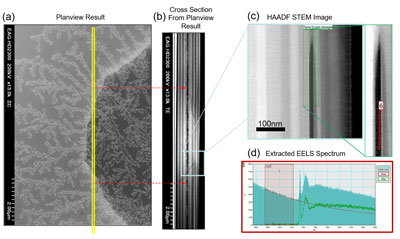
In this study, three different VCSELs were analyzed – two failures and one control. The figure to the right shows STEM analysis on a failed VCSEL device.
This experiment provides a new pathway to diagnose changes in thin oxide aperture layers that may correlate to changes in device performance. Download the application note to learn more.
Would you like to learn more about STEM EELS?
Contact us today for your STEM EELS needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.