Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Services
Home » Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Services
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) is an analytical technique that detects very low concentrations of dopants and impurities. It can provide elemental depth profiles over a depth range from a few nanometers to tens of microns. SIMS works by sputtering the sample surface with a focused beam of primary ions. Secondary ions formed during the sputtering are extracted and analyzed using a mass spectrometer. These secondary ions can range from matrix levels down to parts-per-billion (ppba) levels.
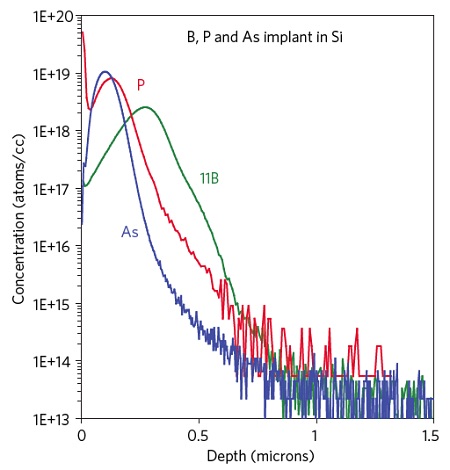
Figure 1 shows Profiles of B, P and As implant standards in Si. These standards are calibrated with NIST SRM. SIMS profiles provide accuracy doping concentrations vs. depth, with excellent detection sensitivity and dynamic range.
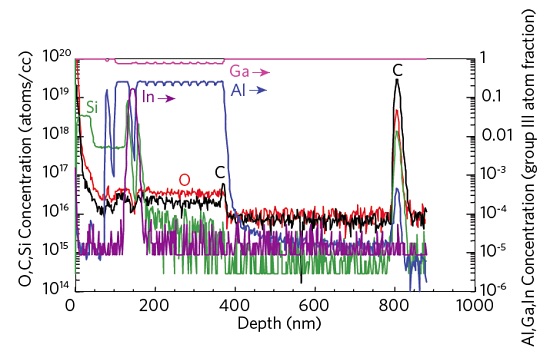
Figure 2 shows Compound (III-V) semiconductor device characterization, complete with composition and dopant/impurity concentration quantification. The profile is optimized for C and O impurity detection and for good depth resolution.
PRINCIPLES
During a SIMS analysis, the samples are sputtered by a focused energetic primary ion beam (100 eV – 15 keV), either oxygen (O2+) or cesium (Cs+). A fraction of sputtered materials are ionized during the sputtering process.
These secondary ions are extracted from the surface, mass analyzed based on unique mass-to-charge ratio of individual elements, and collected as secondary ion intensities. Since each element (and isotope) in the periodic table has a unique mass-to-charge ratio, this technique can detect every element in the periodic table.
The secondary ion intensities can be converted into concentrations based on analysis of reference standards. By continually monitoring the ions, one can determine the concentration as a function of depth into the sample with minimum distortion to the true in-depth distribution and with very high sensitivity (ppma to ppba).
COMMON APPLICATIONS
The extremely high sensitivity and ability to depth profile make SIMS ideally suited to characterizing semiconductors and other thin film materials. Selected applications include the following:
- Dopant and impurity depth profiling
- Composition and impurity measurements of thin films (SiGe, III-V, and II-VI)
- Ultra-high depth resolution profiling of shallow implants and ultra-thin films (ULE implants and gate oxides)
- Bulk analysis, including B, C, O, and N in Si
- High-precision matching of process tools (ion implanters)
- Contaminant profiles in thin films (metals, dieletric)
- Thin film layer structures
- Interface contaminant profiles
STRENGTHS
- Excellent detection sensitivity for dopants and impurities, with ppma or lower detection sensitivity for most elements
- Depth profiles with excellent detection limits and depth resolution
- Small-area analysis (10 µm or larger)
- Detection of all elements and isotopes, including H
- Excellent dynamic range (up to 7 orders of magnitude)
- Major element composition possible, in some applications
LIMITATIONS
- Standards required for accurate quantification
- Element specific (not a survey technique)
- No chemical bonding information
- Destructive
TECHNIQUE COMPARISONS
Other surface analytical techniques that can determine compositional depth profiles include X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Auger electron spectroscopy. Both have poor detection sensitivity (~0.1%) compared with SIMS. Glow discharge mass spectrometry (GDMS) has good sensitivity but it is primarily a bulk technique. Time-of-flight SIMS operates on the same basic principles as SIMS, but experiments are typically limited to the outer monolayers of a sample and are generally not quantitative.
SIMS AT EAG
EAG is the industry standard for SIMS analysis, offering the best detection sensitivity along with accurate concentration and layer structure identification. No other analytical laboratory can match EAG’s depth and breadth of experience and dedication to research and development in the SIMS field. We have the largest number of SIMS instruments worldwide (more than 40 SIMS instruments), highly qualified scientists, and the world’s largest reference material library of over five-thousand ion-implanted and bulk-doped standards for accurate SIMS quantification. EAG has been doing SIMS for over thirty years; longer than any other commercial laboratory.
Would you like to learn more about Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS)?
Contact us today for your Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Services needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.