Implementing Extractables and Leachables into Quality Control Testing Programs
Home » Implementing Extractables and Leachables into Quality Control Testing Programs
One of the many challenges of E&L programs is encountered when the testing transitions from the E&L lab to a routine QC environment. Initial E&L work is typically performed by specialized labs with specialized equipment/personnel which may not be conducive to routine QC testing. Understanding the limitations and challenges of the routine QC environment is key to avoid issues down the road. This presentation will cover the following areas, along with representative case studies are:
- QC method development: How to design the development with the QC lab in mind to ensure success
- Method Validation: How to perform validations for E&L methods and common challenges
- Stability Programs: How to implement stability testing and what does the data mean
- Release Testing: Testing the final product vs. testing incoming components
BACKGROUND
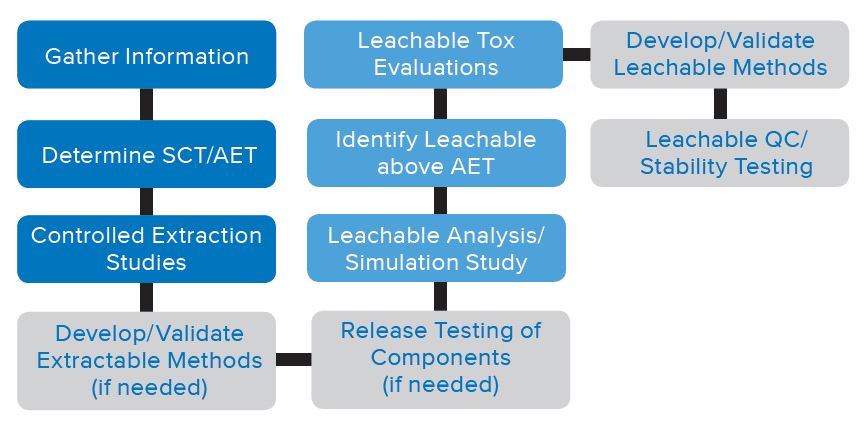
The initial steps of an E&L study are often performed using generic scanning methods utilizing specialized equipment in an R&D lab environment. These methods are typically not fully validated and are used primarily for the determination and identification of extractables and leachables observed. The E&L program continues beyond the initial steps and in many cases programs are required to move the E&L program from the R&D lab and into the QC lab. Figure 1 represents a typical E&L program. The sections in green highlight the QC steps which move into the QC testing arena. The two areas in which you may be required to institute QC testing are:
- When required to set up incoming release testing of components
- When required to set up release and/or stability testing on your final product or API
INCOMING COMPONENT RELEASE TESTING
You may be required to set up incoming testing on the container/ closure components depending on the results of the controlled extraction studies and depending on the testing performed by the manufacturer. These methods should be validated generally in accordance with ICH guidelines:
QUANTITATIVE METHOD
- Accuracy, Precision, Linearity, Specificity, Sensitivity, Limit of Quantitation
LIMITS TEST METHOD
- Specificity, LOD
LEACHABLE TEST METHODS
Establishing QC leachable method may not always be required, there are multiple cases where it may be possible to justify not establishing leachable QC testing.
- No extractable peaks detected. If no peaks are observed under the worst case scenarios it is possible to justify not pursuing any additional testing.
- All extractable peaks are below reporting analytical evaluation threshold.
- The threshold is established based on the safety concern threshold and any peaks observed below the threshold are considered to have minimal risk of having a toxilogical aect.
- No leachables above reporting threshold
- Extractable/Leachable found has no toxic concerns
- Identified extractables/leachables found above the safety concern threshold should be evaluated for potential toxic affects by performing a QSAR analysis or performing a paper tox assessment if tox information is already available on the compound
- If required to establish QC leachable methods, the methods should be validated in accordance with ICH guidelines. Leachables are considered as impurities in the final Drug Product and as such the method should be validated identically as one would validate a DP impurities method:
- There are two typical types of methods which may be employed: Quantitative and a limits test. The specific validate parameters are listed below:
- Quantitative
- Accuracy, Precision, Intermediate Precision, Linearity, Specificity, Sensitivity, Limit of Quantitation, Limit of Detection, Robustness, Solution Stability
- Limits Test
- Specificity, LOD
CHALLENGES OF E&L METHODS
Due to the unique nature of the extractables/leachables and the methods typically employed there are many challenges associated with establishing QC testing methods for extractables and leachables testing
- Don’t expect extractables and Leachables to behave as API/DP related impurities. API and DP related impurities are typically related species which behave similary. Leachables can be a wide variety of compounds ranging from small polar solvents to large macromolecules. As a result their behaviors can be substantially dierent than the “normal” impurities.
- Don’t blindly set “typical” acceptance criterion for the method validations based on similar criteria that might be used for DP related impurities. Critieria need to be set on the required performance of the method and the limitations associated with it.
- Method development may be extensive and complex.
- May not be able to identify all leachables. They may not mass spec well or have diculty in isolating.
- Analytical levels can be significantly lower than ICH impurity levels. In typical cases it is not uncommon for leachables to be 10-100X lower than impurity reporting levels.
- API and Formulation impurity interferences. Due to the low levels which leachables are needed to be monitored to, API impurities and formulations impurities which typically may not be observable may cause interference with the leachable peaks.
- To reach to the low analytical levels it is not uncommon to have to perform sample concentration steps in order to obtain the needed AET. The concertation can range from 2X to 100X in some cases. This can lead to challenges with some formulations as they may gel/solidify or precipitate out.
- Many of the identified leachables may not have any commercially available standards available, making validating methods dicult.
METHOD VALIDATION CHALLENGES
SPECIFICITY
- API/DP degradants can cause significant issues. Not only the impurities that are known, but due to the significantly lower levels which leachables are required to go down to, it is not uncommon to observe significantly more API/DP related impurities than what the normal impurity methods monitor for. As a result it is highly recommended that aged API/DP is used to track these impurities. If aged material is not available, stressing the API/DP to artificially generate impurities should be performed.
- Formulation/placebo impurities need to be accounted for as well. As with the API/DP impurities, it is not atypical to observe significantly more excipient related peaks that expected.
- Co-elution of extractables/leachables can be a challenge. In some cases the leachables being monitored for may have extremely similar chemical structures making their chromatographic separation challenging if even possible. In some cases it may not be possible to completely separat e the leachable.
ACCURACY/PRECISION
- Non-Homogeneous samples are a challenge. Whether testing DP or extracts the variance in the samples can be significantly greater than one might expect for API/ DP related impurities. This can make performing sample precision testing more challenging as it can result in testing the variance of the samples rather than the method.
- Traditional precision testing is typically performed by preparing multiple replicated from lots of material. However, leachable may not be present in the lot until it has aged long enough for them to be present.
- Using spiked samples (homogenized) can be a preferred way to perform both accuracy and precision testing of the method. This would involve preparing three levels across the range of the method prepared in triplicate. The precision is determined by calculated the %RSD of the recoveries.
- Use internal standards/surrogate standards as needed and especially when actual standards of the leachables are not available.
CHALLENGES/CAUTIONS
There are some challenges/cautions to be considered when using surrogate/internal standards.
- They should be carefully chosen based on what is known of the target compounds.
- If a range of leachable is being monitored for it may be appropriate to use multiple standards rather than a single standard in order to cover the potential range of the various leachable compounds.
STANDARDS
Surrogate/internal standards may not mimic behavior of actual extractables/leachables and as a result the method may have issues later down the road during routine testing.
- Wider acceptance ranges than would be applied to API/DP related impurities may be justifiable based on the performance of the method and the intent of the testing.
LINEARITY
- Use standards of the known leachable (if available) and surrogates and/or internal standards if no other standards are available.
- Some of the analytical techniques are inherently non-linear and will require special treatment. This can be accomplished either by transforming the responses to generate a linear curve or fitting the curve with a non-linear regression analysis. These techniques may be able to be fit with a linear regression under smaller ranges of use and approximate a linear response. Some of the common techniques which can generate nonlinear curves are:
- Mass Spectrometry
- Corona Aerosol Detector (CAD)
- Evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD)
SOLUTION STABILITY
Some extractables/leachables inherently unstable or reactive making monitoring and setting solution stability ranges a challenge. For example the anti-oxidant Irgafos 168 readily oxidizes to form “oxidized irgafos 168”. It is difficult to control or prevent the oxidation from occurring and is commonly accepted that if you observe one you will have the other as well.
LEACHABLE TEST METHODS
Establishing QC leachable method may not always be required, there are multiple cases where it may be possible to justify not establishing leachable QC testing.
- No extractable peaks detected. If no peaks are observed under the worst case scenarios it is possible to justify not pursuing any additional testing.
- All extractable peaks are below reporting analytical evaluation threshold.
- The threshold is established based on the safety concern threshold and any peaks observed below the threshold are considered to have minimal risk of having a toxilogical aect.
- No leachables above reporting threshold
- Extractable/Leachable found has no toxic concerns
- Identified extractables/leachables found above the safety concern threshold should be evaluated for potential toxic affects by performing a QSAR analysis or performing a paper tox assessment if tox information is already available on the compound
- If required to establish QC leachable methods, the methods should be validated in accordance with ICH guidelines. Leachables are considered as impurities in the final Drug Product and as such the method should be validated identically as one would validate a DP impurities method:
- There are two typical types of methods which may be employed: Quantitative and a limits test. The specific validate parameters are listed below:
- Quantitative
- Accuracy, Precision, Intermediate Precision, Linearity, Specificity, Sensitivity, Limit of Quantitation, Limit of Detection, Robustness, Solution Stability
- Limits Test
- Specificity, LOD
CHALLENGES OF E&L METHODS
Due to the unique nature of the extractables/leachables and the methods typically employed there are many challenges associated with establishing QC testing methods for extractables and leachables testing
- Don’t expect extractables and Leachables to behave as API/DP related impurities. API and DP related impurities are typically related species which behave similary. Leachables can be a wide variety of compounds ranging from small polar solvents to large macromolecules. As a result their behaviors can be substantially dierent than the “normal” impurities.
- Don’t blindly set “typical” acceptance criterion for the method validations based on similar criteria that might be used for DP related impurities. Critieria need to be set on the required performance of the method and the limitations associated with it.
- Method development may be extensive and complex.
- May not be able to identify all leachables. They may not mass spec well or have diculty in isolating.
- Analytical levels can be significantly lower than ICH impurity levels. In typical cases it is not uncommon for leachables to be 10-100X lower than impurity reporting levels.
- API and Formulation impurity interferences. Due to the low levels which leachables are needed to be monitored to, API impurities and formulations impurities which typically may not be observable may cause interference with the leachable peaks.
- To reach to the low analytical levels it is not uncommon to have to perform sample concentration steps in order to obtain the needed AET. The concertation can range from 2X to 100X in some cases. This can lead to challenges with some formulations as they may gel/solidify or precipitate out.
- Many of the identified leachables may not have any commercially available standards available, making validating methods dicult.
METHOD VALIDATION CHALLENGES
SPECIFICITY
- API/DP degradants can cause significant issues. Not only the impurities that are known, but due to the significantly lower levels which leachables are required to go down to, it is not uncommon to observe significantly more API/DP related impurities than what the normal impurity methods monitor for. As a result it is highly recommended that aged API/DP is used to track these impurities. If aged material is not available, stressing the API/DP to artificially generate impurities should be performed.
- Formulation/placebo impurities need to be accounted for as well. As with the API/DP impurities, it is not atypical to observe significantly more excipient related peaks that expected.
- Co-elution of extractables/leachables can be a challenge. In some cases the leachables being monitored for may have extremely similar chemical structures making their chromatographic separation challenging if even possible. In some cases it may not be possible to completely separat e the leachable.
ACCURACY/PRECISION
- Non-Homogeneous samples are a challenge. Whether testing DP or extracts the variance in the samples can be significantly greater than one might expect for API/ DP related impurities. This can make performing sample precision testing more challenging as it can result in testing the variance of the samples rather than the method.
- Traditional precision testing is typically performed by preparing multiple replicated from lots of material. However, leachable may not be present in the lot until it has aged long enough for them to be present.
- Using spiked samples (homogenized) can be a preferred way to perform both accuracy and precision testing of the method. This would involve preparing three levels across the range of the method prepared in triplicate. The precision is determined by calculated the %RSD of the recoveries.
- Use internal standards/surrogate standards as needed and especially when actual standards of the leachables are not available.
CHALLENGES/CAUTIONS
There are some challenges/cautions to be considered when using surrogate/internal standards.
- They should be carefully chosen based on what is known of the target compounds.
- If a range of leachable is being monitored for it may be appropriate to use multiple standards rather than a single standard in order to cover the potential range of the various leachable compounds.
STANDARDS
Surrogate/internal standards may not mimic behavior of actual extractables/leachables and as a result the method may have issues later down the road during routine testing.
- Wider acceptance ranges than would be applied to API/DP related impurities may be justifiable based on the performance of the method and the intent of the testing.
LINEARITY
- Use standards of the known leachable (if available) and surrogates and/or internal standards if no other standards are available.
- Some of the analytical techniques are inherently non-linear and will require special treatment. This can be accomplished either by transforming the responses to generate a linear curve or fitting the curve with a non-linear regression analysis. These techniques may be able to be fit with a linear regression under smaller ranges of use and approximate a linear response. Some of the common techniques which can generate nonlinear curves are:
- Mass Spectrometry
- Corona Aerosol Detector (CAD)
- Evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD)
SOLUTION STABILITY
Some extractables/leachables inherently unstable or reactive making monitoring and setting solution stability ranges a challenge. For example the anti-oxidant Irgafos 168 readily oxidizes to form “oxidized irgafos 168”. It is difficult to control or prevent the oxidation from occurring and is commonly accepted that if you observe one you will have the other as well.
STABILITY PROGRAMS
Stability programs for leachables (if needed) should be established per ICH Q1 guidelines. Testing under both nominal storage conditions and accelerated conditions. However, the data interpretation can be more complex and needs to be evaluated separately from normal API/DP related impurities.
- Arrhenius equation doesn’t apply.
There are two main forces which determine if a compound will leach into a drug product.
- Migration kinetics – the rate at which the will migrate through the material. This rate is temperature dependent.
- Solubility/Partitioning – this is the ratio of how soluble the compound is in the DP formulation and how soluble the compound is in the component material. While the solubilities due vary with temperature, they won’t vary proportionally and it is possible that the material solubility increases greater than DP formulation solubility resulting in the potential that a leachable will be observed at higher levels under lower temperatures.
Regression analysis can be used to model the rate at which leachable appear but the resulting kinetic curves can be significantly different than typical reaction kinetics.
EXTRACTABLE – LEACHABLE CORRELATION
If possible one of the main goals of an E&L program should be to establish the extractable to leachable correlation. What this means is that enough data is generated and the leaching is understood to the point that you can directly relate the observed leachable level to the known extractable level of the component.
- For example based on the data sets, it may be possible to correlate that if a component have a compound that extracts 30 μg this will equate to a total of 2 μg of the component leaching into the product.
- If it is possible to establish an extractable to leachable correlation it may be possible to either reduce or eliminate the leachable testing and establish control of the leachable by controlling the extractable in the incoming material.
SUMMARY
E&L methods can pose a series of challenges when they transition from the R&D environment an into the realm of routine QC testing. It is important to understand these challenges and limitation prior to implementing avoid costly delays as a result of validation failures or QC investigations as a result of poorly developed/validated methods or poorly established routine testing protocols.
Would you like to learn more about Implementing Extractables and Leachables?
Contact us today for your extractable and leachable needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.